Embedded Wallets
Discover Okto's Embedded Wallets: self-custodial wallets seamlessly integrated into your application via the Okto SDK. Learn how Wallet Providers define distinct ecosystems and control interoperability for enhanced user experience and security.
What are Okto Embedded Wallets?
Okto Embedded Wallets offer a streamlined way to bring Web3 capabilities to your users directly within your application. Unlike standalone wallets or browser extensions, Okto embedded wallets are directly built into the application, offering an intuitive user experience. They are:
- Self-Custodial: Users maintain full control over their keys and assets. Okto's infrastructure utilizes technologies like Multi-Party Computation (MPC) to manage keys securely, ensuring private keys are never fully exposed in one place.
- Seamlessly Integrated: Created and managed via the Okto SDKs, eliminating the need for users to install external wallet extensions or manage complex setups.
- User-Friendly: Designed to simplify onboarding, offering familiar Web2-like login and interaction experiences (e.g., email, social login), often removing the need for users to manage seed phrases directly.
- Automatically Provisioned: Wallets are typically created automatically for users across supported chains upon successful authentication with your application via Okto.
Developers can leverage Okto’s SDKs to easily build embedded wallets into their apps, whether on web or mobile platforms. These wallets bring the power of Okto's infrastructure to end users, hiding blockchain complexities and enabling seamless asset management.
Key Features of Okto Embedded Wallets
- Unified Asset Management: Users can view and manage assets across multiple supported chains (e.g., Ethereum, Solana, Aptos) in a single wallet interface within your application.
- Chain-Abstracted Transactions: By leveraging Okto's backend infrastructure (including the Unified Liquidity Layer for swaps), embedded wallets allow users to transact without needing to deeply understand the underlying chains, token standards, or manually manage gas fees in many scenarios.
- Simplified Onboarding: Integrated with familiar authentication methods, embedded wallets make onboarding simple for users with no prior blockchain experience.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Okto's embedded wallets are designed to work seamlessly across web and mobile environments where SDKs are integrated, providing consistent functionality.
- Advanced Security: Leveraging MPC technology, Okto embedded wallets enhance security by distributing key management processes, reducing single points of failure.
The Wallet Provider Ecosystem
A core concept for understanding Okto Embedded Wallets is the Wallet Provider (WP). A Wallet Provider defines a distinct ecosystem for wallets and manages the underlying infrastructure.
-
Okto's Role: Okto itself provides foundational Wallet Providers, currently including:
- Okto EOA Wallets: Utilising standard Externally Owned Accounts for EVM type chains.
- Okto AA Wallets: Leveraging Account Abstraction (ERC-4337) for smart contract wallets with enhanced features for EVM type chains.
Note
After Pectra Okto will merge both EoA and AA into a single WP.
-
Client Association: Each Client application integrating Okto is associated with one specific Wallet Provider.
-
User Association: A single user (identified by their login method) can interact with multiple Client applications. These applications might belong to the same Wallet Provider or different Wallet Providers.
(Future Scope: In the future, third-party entities or specific clients might operate as distinct Wallet Providers within the Okto framework, creating their own unique wallet ecosystems.)
Interoperability
The most critical aspect defined by the Wallet Provider is interoperability.
To understand Okto's specific approach, it's helpful to first consider the general notion of interoperability. In blockchain, interoperability often refers to a single wallet's ability to move assets or interact seamlessly across different blockchain systems.
Okto's embedded wallet interoperability extends this idea: different client applications operating under the same Wallet Provider (WP) can offer the exact same wallet and assets to a common user. This creates a unified experience for the user within that specific Wallet Provider's ecosystem.
Important Note
Interoperability for embedded wallets is currently a choice for clients, with the default being a non-interoperable setup where each client acts as its own Wallet Provider. If a client desires interoperability, they will need to reach out to the Okto team. In the future, the Okto dashboard will provide an option for clients to choose whether they want to be part of an interoperable system or operate as their own Wallet Provider, based on their specific use case.
Note
Embedded wallets are only interoperable within the same Wallet Provider ecosystem.
This means:
1. Within the SAME Wallet Provider Ecosystem
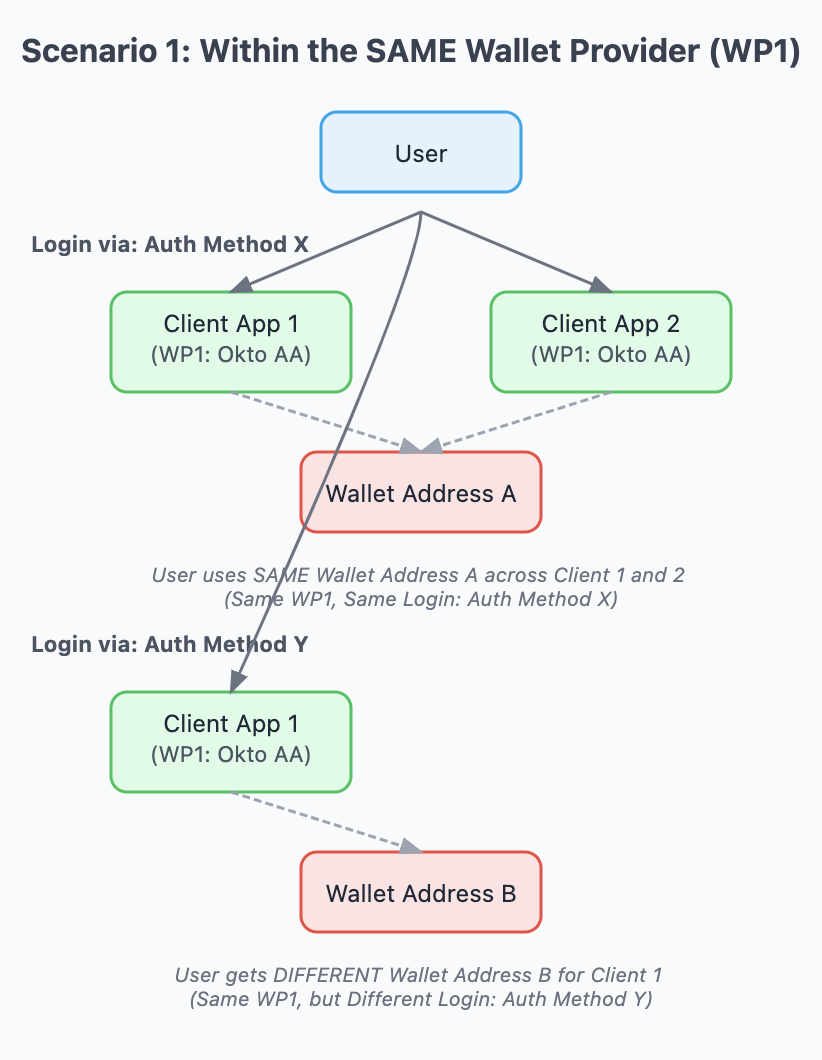
- If a user interacts with multiple client applications (e.g., Client App 1 and Client App 2 using Google Authentication) that both belong to the same Wallet Provider (e.g., both use Okto AA wallets), they will use the exact same wallet address (e.g., Address
A) across both applications for any given blockchain. - Assets acquired in Client App 1 within this WP ecosystem are directly accessible and usable in Client App 2, providing a seamless and unified multi-app experience for the user.
Note
- A user's wallet address is typically derived from or linked to their authentication method (e.g., GAuth, email OTP).
- If a user switches to a different login mechanism (e.g., from Google login to email OTP), this will generally result in a different set of wallet addresses, even if the client applications are under the same Wallet Provider. The consistent wallet address sharing described above applies when the user employs the same login mechanism across clients within that single WP.
- In summary, a user's address via the same login mechanism will remain the same under a single WP, regardless of which client app they log in to, as long as the client is under that WP as well.
2. Across DIFFERENT Wallet Provider Ecosystems
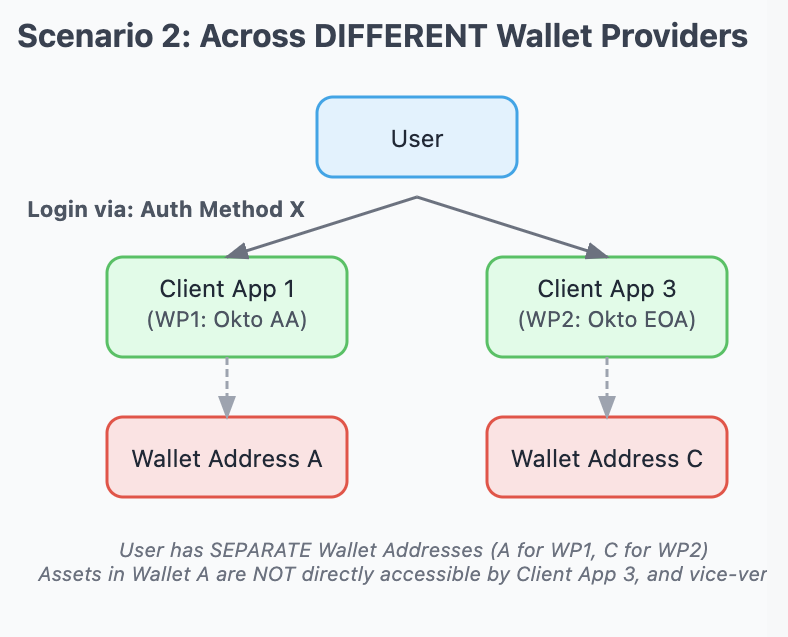
- If the same user (potentially identified by the same login credentials but for clients under different WPs) interacts with Client App 1 (under WP 1, e.g., Okto AA) and Client App 2 (under WP 2, e.g., Okto EOA or a future third-party WP), they will have completely separate wallet addresses for each ecosystem (e.g., Address A for WP 1, Address B for WP 2).
- These wallets are non-interoperable from a direct client access perspective. This means assets held in the wallet associated with WP 1 (Address
A) cannot be directly viewed or utilized by Client App 2, which operates exclusively within the WP 2 ecosystem (Address B), and vice-versa. They are distinct wallets tied to the same user identity but siloed by the Wallet Provider.
Note
- When we state that wallets across different Wallet Providers are "non-interoperable" in this context, we mean that the direct access and visibility of assets are siloed within each WP's ecosystem for client applications.
- However, each embedded wallet (e.g., Address A under WP1, or Address B under WP2), once provisioned, still functions as a standard self-custodial wallet with the traditional notion of interoperability. The wallets are still capable of standard blockchain transactions and can take advatage of Okto's full suite of features..
- The "non-interoperability" refers to the barrier between client applications belonging to different Wallet Provider ecosystems in terms of shared asset views and direct utilization.
Okto's Current Wallet Providers
Okto currently offers two primary Wallet Provider types for embedded wallets:
1. Okto EOA Wallets
- Type: Standard Externally Owned Accounts for EVM-type chains. (Note: Non-EVM ecosystems like Solana and Aptos typically have standard programmable wallets which may have different characteristics).
- Generation: Automatically generated for users upon authentication by default.
- Interoperability: Wallets are interoperable across different client applications that utilize the Okto EOA Wallet Provider (when using the same login mechanism).
2. Okto AA Wallets
- Type: Smart Contract Wallets based on Account Abstraction (ERC-4337) for EVM-type chains. (Note: Non-EVM ecosystems like Solana and Aptos typically have standard programmable wallets which may have different characteristics).
- Benefits: Enable features like gas sponsorship, batched transactions, social recovery, and enhanced policy controls.
- Generation: Automatically generated for users upon authentication.
- Interoperability: Wallets are interoperable across different client applications that utilize the Okto AA Wallet Provider (when using the same login mechanism).
Special Case: JWT/OAuth Users
Users authenticating via methods like JWT or certain specific OAuth providers might function within a more isolated or client-specific context. In such cases, their wallets can be considered as operating under a special Wallet Provider instance unique to that authentication context and client, potentially limiting interoperability even with other clients that might generally share a common WP (like Okto AA or Okto EOA).
Use Cases of Embedded Wallets
1. Web2 Applications
Web2 applications are traditional, centralized web services that most internet users are familiar with. Integrating embedded wallets into these applications can introduce blockchain features without overhauling the entire platform. Here's how embedded wallets enhance Web2 apps:
- Cryptocurrency Payments: E-commerce platforms or service-based websites can integrate embedded wallets to accept cryptocurrency payments. Users can make purchases or subscriptions using digital assets without leaving the familiar interface of the Web2 application.
- Tokenized Rewards: Loyalty programs can use embedded wallets to distribute and manage tokenized rewards. Users earn, store, and redeem these tokens within the app, providing a seamless rewards experience enhanced by blockchain technology.
- NFT Integration: Media platforms, social networks, or content creation sites can use embedded wallets to allow users to mint, buy, sell, or showcase Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). This brings the world of digital collectibles into traditional web spaces.
- Blockchain-based Identity: Web2 applications can leverage embedded wallets for decentralized identity solutions. Users can manage their digital identity and credentials within the app, potentially using them across multiple services.
2. Web3 Applications
Web3 applications are decentralized apps (dApps) built on blockchain technology. Embedded wallets in this context aim to simplify the often complex user experience associated with Web3. Here's how they're utilized:
- Simplified dApp Interactions: Embedded wallets allow users to interact with smart contracts, decentralized exchanges, or other blockchain services directly within the dApp interface. This eliminates the need to switch between the dApp and a separate wallet application.
- Gas Fee Management: Embedded wallets can handle gas fee calculations and payments behind the scenes, simplifying one of the most confusing aspects of blockchain interactions for many users.
- Multi-chain Support: Advanced embedded wallet solutions can manage assets and interactions across multiple blockchain networks, all from within a single dApp interface.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Access: DeFi platforms can use embedded wallets to provide seamless access to complex financial operations like lending, borrowing, or yield farming, making these services more accessible to a broader audience.
- Governance Participation: DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) and other blockchain-based governance systems can use embedded wallets to simplify the process of voting and participating in governance decisions.
Bridging Web2 and Web3
Embedded wallets play a crucial role in bridging the gap between Web2 and Web3:
- Gradual Adoption: They allow Web2 applications to gradually adopt blockchain features without alienating users unfamiliar with crypto.
- Familiar UX: By integrating blockchain functionality seamlessly, embedded wallets maintain a familiar user experience while introducing powerful Web3 capabilities.
- Reduced Friction: Embedded wallets significantly reduce the friction of onboarding new users to Web3, as they don't require separate wallet creation or management.
- Interoperability: Advanced embedded wallet solutions can offer interoperability between Web2 and Web3 ecosystems, allowing users to leverage their digital assets across various platforms.
By integrating embedded wallets, both Web2 and Web3 applications can offer enhanced functionality, improved user experiences, and easier access to blockchain technology. This integration is a key step in the broader adoption of Web3 technologies across the digital landscape.
Interoperable vs. Closed-Loop Wallets
When it comes to embedded wallets, there are two main types: interoperable wallets and closed-loop wallets. Understanding the differences between these two can help developers and users choose the right solution for their needs.
Interoperable Wallets
Interoperable wallets are designed to work across multiple platforms, networks, and applications. They offer flexibility and broad compatibility within the blockchain ecosystem.
Key Features
- Multi-Chain Support: Interoperable wallets can manage assets across various blockchain networks, such as Ethereum, Solana, and Polygon.
- Cross-Platform Functionality: Users can access their wallet across different applications and services, maintaining a consistent identity and asset portfolio.
- Broad Asset Support: These wallets typically support a wide range of cryptocurrencies and tokens, including those from different blockchain ecosystems.
- DApp Compatibility: Users can interact with various decentralized applications (DApps) using the same wallet.
- Unified User Experience: Despite working across multiple platforms, interoperable wallets strive to provide a consistent user interface and experience.
Closed-Loop Wallets
Closed-loop wallets are restricted to a specific platform, application, or network. They offer a more controlled and often simplified user experience within a particular ecosystem.
Key Features
- Platform-Specific: Designed to work within a single application or a limited set of related applications.
- Tailored Functionality: Features are often customized to suit the specific needs of the platform or application.
- Simplified Asset Management: Usually support a limited range of assets relevant to the specific ecosystem.
- Integrated User Experience: Deeply integrated with the host application, providing a seamless and cohesive user experience.
- Controlled Environment: Offer more control over user interactions and asset movements within the defined ecosystem.
The choice between interoperable and closed-loop wallets largely depends on the specific needs of the application and its users. Interoperable wallets are ideal for applications that aim to provide users with access to the broader blockchain ecosystem. On the other hand, Closed-loop wallets are more suitable for applications with specific, contained use cases.
Okto SDK Wallets are Interoperable Wallets, allowing for flexibility and broad ecosystem integration. This aligns with our goal of making blockchain technology more accessible and user-friendly across various applications and use cases.