Architecture
Understand the technical architecture of the Trade Service
Trade Service Architecture
While the Unified Liquidity Layer (ULL) provides the core infrastructure for cross-chain token transfers, the Trade Service builds on top of this foundation to deliver a comprehensive, user-friendly token swap experience. This page explains how the Trade Service extends ULL's capabilities and simplifies integration for developers.
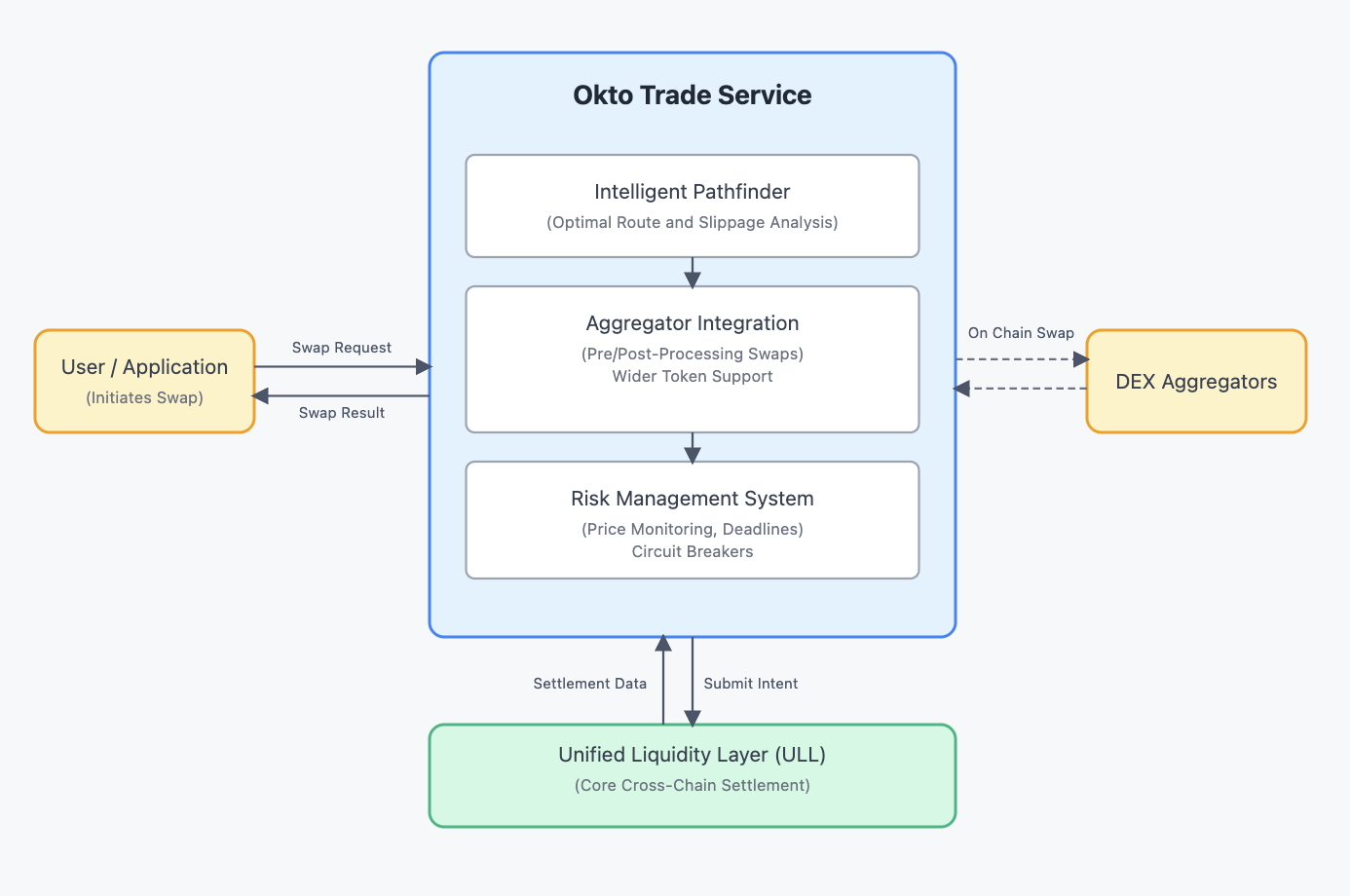
Core Components
The Trade Service consists of several specialized components that work alongside ULL:
1. Intelligent Pathfinder
The Pathfinder is a sophisticated routing engine that analyzes all possible paths between source and destination tokens. It considers factors like:
- Price impact and slippage
- Gas costs across chains
- Execution speed
- Security considerations
- Current market conditions
Based on this analysis, it determines the optimal route for each swap—which might involve direct ULL transfers, additional aggregator steps, or a combination of both.
2. Aggregator Integration
While ULL efficiently handles transfers of major assets across chains, the Trade Service extends this to support virtually any token through smart integrations with various DEX aggregators and bridges.
For a complex swap like "TOKEN-A on Chain 1 to TOKEN-B on Chain 2" where neither token is directly supported by ULL, the Trade Service orchestrates a sequence like:
- Pre-processing: Convert TOKEN-A to a ULL-supported token (e.g., USDC) on Chain 1 with the help of a DEX aggregator.
- Cross-chain Transfer: Move USDC from Chain 1 to Chain 2 via ULL
- Post-processing: Convert USDC to TOKEN-B on Chain 2
This entire multi-step process is abstracted into a single, simple request for the end user.
3. Risk Management System
The Trade Service implements a comprehensive risk management system to protect users and ensure reliable operation.
Risk Mitigation Features:
- Real-time Price Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of price feeds to detect anomalies
- Slippage Protection: User-defined slippage parameters with reasonable defaults
- Transaction Deadlines: Automatic expiration for stale transactions
- Circuit Breakers: Automatic suspension of trading during extreme market conditions
How Trade Service and ULL Work Together
The Trade Service and ULL form a powerful partnership that leverages their respective strengths:
Complementary Roles:
- Trade Service: Provides the easy to integrate APIs, user-facing interface, token support, and intelligent routing
- ULL: Serves as the core execution engine that drives cross-chain settlements
Typical Flow:
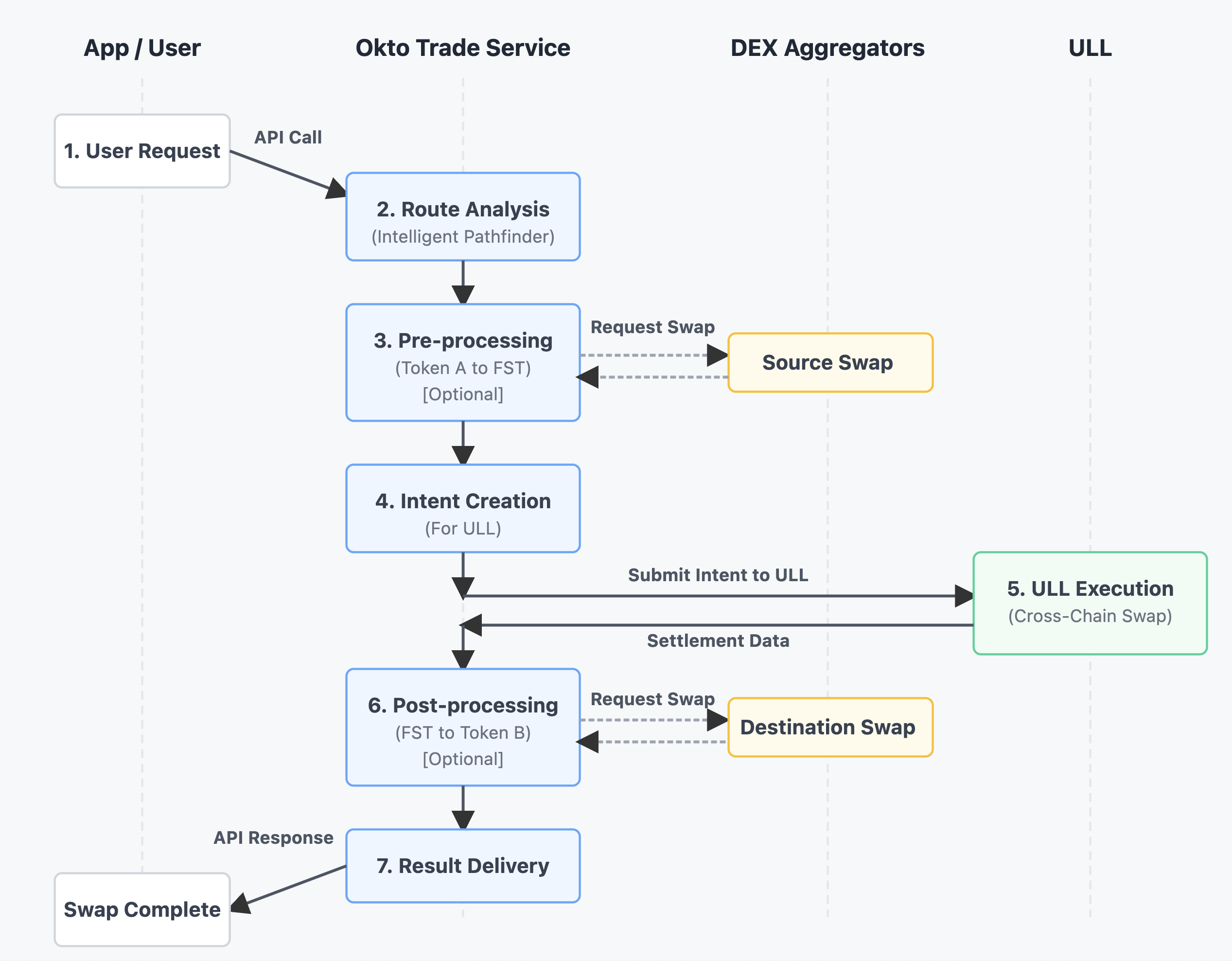
- User Request: Application calls Trade Service API with swap parameters
- Route Analysis: Trade Service analyzes the request and determines optimal path
- Pre-processing: If needed, Trade Service prepares token conversion steps
- Intent Creation: Trade Service creates a formal intent structure for the core cross-chain transfer
- ULL Execution: The intent is passed to ULL for cross-chain settlement
- Post-processing: If needed, Trade Service completes final token conversions
- Result Delivery: The completed transaction details are returned to the application
Throughout this process, ULL handles the secure cross-chain asset movement while Trade Service manages the end-to-end user experience.