Decentralized Transaction Network (DTN)
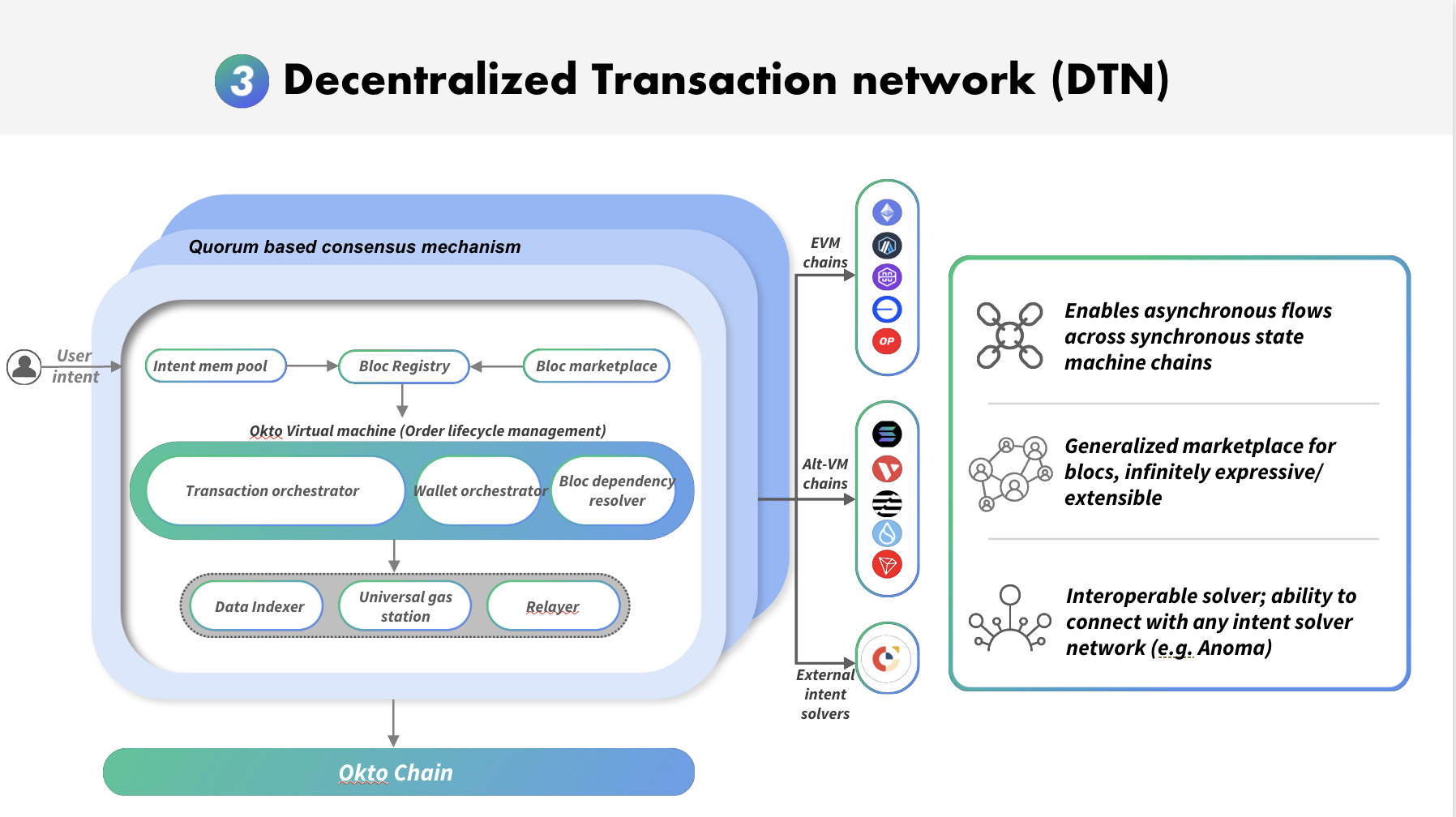
The Decentralized Transaction Network (DTN) is Okto's execution layer that coordinates multi-chain operations by translating user-defined high-level intents into actionable sub-transactions across multiple blockchains. It serves as the intelligent coordinator that breaks down complex cross-chain operations into manageable steps, integrating with the DWN for secure authorization and the ULL for liquidity management.
Core Functionality
The DTN's primary function is to interpret and execute user intents that span multiple blockchains. It breaks down complex requests into manageable sub-transactions, coordinates with other Okto components (DWN, ULL), and ensures the successful and verifiable execution of cross-chain operations.
Similar to a highly specialized travel agent that consolidates multi-destination trips across several countries, the DTN consolidates cross-chain tasks—such as bridging, swapping, or staking—into a single, streamlined process. By orchestrating sub-transactions and handling execution behind the scenes, DTN renders multi-chain interactions as intuitive as any traditional web-based application.
Key functionalities include:
-
Intent-Driven Execution: Breaks down a complex user intent (e.g., a multi-chain token swap) into sub-transactions that can be executed independently on target chains.
-
Asynchronous Transaction Management: Manages sub-transactions asynchronously, optimizing for speed and efficiency across chains with varying confirmation times.
-
Unified Liquidity Layer (ULL) Interaction: Leverages the ULL to identify and utilize optimal optimal liquidity route for each sub-transaction, ensuring cost-effectiveness and efficiency.
-
Decentralized Wallet Network (DWN) Coordination: Collaborates with the DWN to securely obtain transaction signatures.
-
On-Chain Verification and Transparency: Commits transaction payloads and execution status to the Okto Chain, providing an immutable and auditable record of all DTN operations.
-
Error Handling and Retries: Implements error handling and automated retry mechanisms to ensure transaction completion and resilience to network issues.
Architecture and Technology
Decentralized Node Network
The DTN operates as a network of specialized nodes responsible for bidding on and executing jobs. These nodes are selected via a competitive process based on performance, cost efficiency, and reputation.
Currently, Okto operates these nodes to maintain consistent performance and early stability. Over time, the architecture will open to independent node operators to further decentralize execution, with each node competing for jobs on-chain and earning fees for successful execution.
Asynchronous Transaction Management
The DTN employs an asynchronous model to manage sub-transactions across different chains, accommodating varying confirmation times and network latencies. This allows for:
- Parallel Execution: Running compatible operations simultaneously across different chains
- Sequential Coordination: Ensuring dependent operations execute in the correct order
- Adaptive Timing: Adjusting execution strategies based on network conditions
Key Features
Intent-Based Execution
DTN enables "intent-based transactions" where users specify desired outcomes rather than execution details:
- High-Level Goals: Users declare what they want to accomplish ("swap USDC to ETH and stake")
- Automatic Decomposition: DTN breaks these into specific sub-transactions
- Optimized Execution: DTN handles the technical complexity while users enjoy simple interactions
Comprehensive Transaction Handling
DTN orchestrates the full lifecycle of multi-chain operations:
- User Approvals: Managing consent and authorization flows
- Fee Calculations: Optimizing gas costs across different networks
- Settlement Verification: Ensuring all steps complete successfully
Automatic Error Recovery
Transaction failures can arise from various conditions: network congestion, gas price spikes, or blockchain reorganizations. DTN provides robust fault tolerance through:
- Continuous Monitoring: Tracking the status of each sub-transaction in real-time
- Intelligent Retries: Automatically retrying failed transactions with optimized parameters
Benefits for Users and Developers
For Users:
- Simplified Experience: Complex multi-chain operations become single-click actions
- Reliable Execution: Automatic retry and error handling ensures operations complete successfully
- Cost Optimization: Intelligent routing minimizes fees and execution time
- Complete Transparency: Full audit trail of all operations on-chain
For Developers:
- Reduced Complexity: Focus on application logic instead of cross-chain coordination
- Faster Development: Pre-built Blocs and automated orchestration accelerate integration
- Reliable Infrastructure: Proven execution layer with built-in error handling
- Scalable Architecture: Handle increasing transaction volumes with distributed processing
Getting Started
Ready to leverage DTN's powerful orchestration capabilities?
- Explore Okto SDKs →: Multi-platform SDKs for web and mobile development
- Learn about Intents →: Understand intent-based execution patterns