Decentralized Wallet Network (DWN)
The Decentralized Wallet Network (DWN) is a network of secure, independent nodes that collectively manage user wallets in a trust-minimized manner and unifies multiple blockchains into a single wallet experience. It simplifies blockchain interactions by consolidating various networks into one secure interface while keeping users in complete control of their assets.
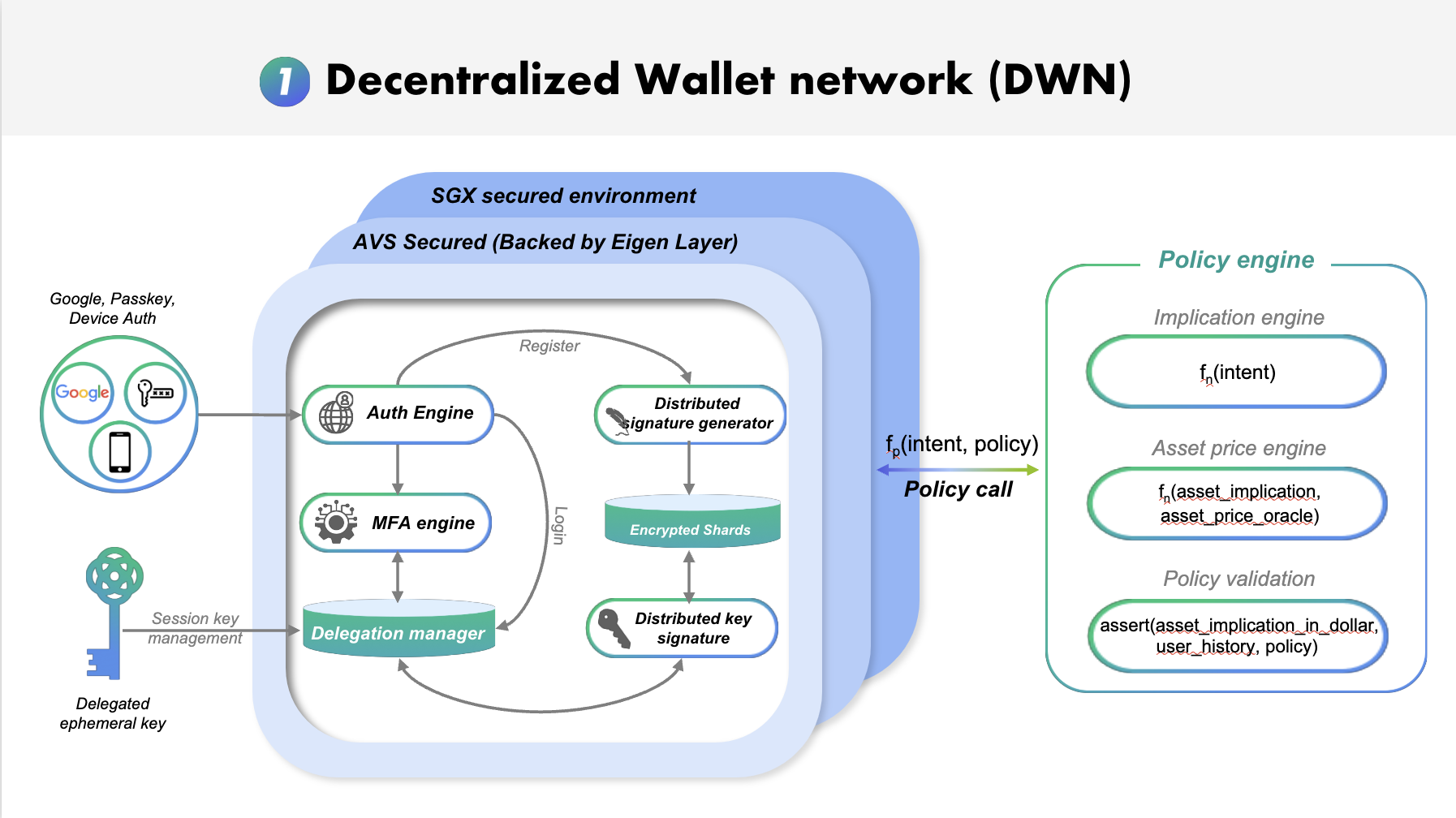
Core Functionality
The DWN's primary function is to provide a secure and decentralized infrastructure for managing user wallets across multiple blockchains. It eliminates the fragmentation and security risks associated with traditional wallet solutions in a multi-chain environment.
Within the Okto infrastructure, the DWN is responsible for two core functions:
- Creating user and client wallets across all supported chains: Acting as a unified gateway for wallet creation across multiple blockchain ecosystems
- Transaction signing: Coordinating a decentralized network of signing nodes to securely authorize transactions without any single point of failure
In simpler terms, the DWN acts as a "universal wallet layer" that hides blockchain intricacies from users. Users retain full control over their funds — no single party (not even Okto) can unilaterally access them — yet dealing with different networks becomes as straightforward as clicking a button.
Key Features
-
Unified Multi-Chain Wallet Experience: Provides users with a single wallet interface to access and manage assets across multiple blockchains, including EVM and non-EVM chains (e.g., Ethereum, Solana, Aptos).
-
Decentralized Key Management: Employs Multi-Party Computation (MPC) and Threshold Signature Schemes (TSS) to distribute private key management across a network of decentralized nodes, eliminating single points of failure and enhancing security.
-
Trust-Minimized Operation: Operates in a trust-minimized manner, ensuring that no single entity, including Okto, has unilateral control over user funds or private keys.
-
User-Friendly Onboarding: Supports Web2-style authentication methods (e.g., Google OAuth, Email OTP, Phone OTP), simplifying user onboarding and eliminating the need for seed phrase management.
-
Secure Transaction Signing: Coordinates a decentralized network of MPC nodes to securely sign transactions on behalf of users, ensuring cryptographic security and user consent.
Architecture and Technology
MPC-TSS (Multi-Party Computation - Threshold Signature Scheme)
MPC-TSS is the backbone of DWN's security model. It is a secure method of signing transactions where a private key is split and distributed among multiple parties, and a threshold number of them must collaborate to generate a signature. The complete private key is never fully revealed. It combines the principles of Multi-Party Computation (MPC) and Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS) to enhance security and privacy.
Okto's implementation employs a 2-of-3 MPC scheme. This means that the network consists of 3 independent nodes and at least 2 nodes must cooperate to sign any transaction. No single entity (including Okto itself) can unilaterally access or control user funds.
EigenLayer AVS (Actively Validated Services)
Perhaps most revolutionary is Okto's use of EigenLayer’s Actively Validated Services (AVS) for its operator nodes. EigenLayer Actively Validated Services (AVS) is a framework that leverages Ethereum's robust security through restaking. Rather than building security from scratch, DWN inherits strong security guarantees from Ethereum's proof-of-stake system. This architecture provides multiple security benefits:
- Network Security: AVS operators must stake significant assets across multiple systems including Ethereum mainnet. This creates a powerful economic deterrent. Any malicious behavior risks their entire staked position, not just within Okto but across the broader EigenLayer ecosystem.
- Independent Operators: The EigenLayer ecosystem ensures node diversity, with validators coming from different organizations and jurisdictions, reducing collusion risks and promoting decentralization.
- Economic Security: By leveraging Ethereum's established security through EigenLayer, Okto gains robust protection without building its own security network from scratch.
Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs)
Each MPC node operates within a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE), like Intel SGX. This isolates sensitive cryptographic operations from the node's main operating system. Even if a node's broader system were breached, the TEE would safeguard the cryptographic processes.
TEEs provide several critical security benefits:
- Hardware-Level Isolation: Cryptographic operations run in an isolated memory region inaccessible to the operating system
- Attestation: Ability to cryptographically verify that the correct, unmodified code is running
- Sealed Storage: Protects sensitive data like key shares from unauthorized access
This multilayered approach, combining cryptographic security (MPC-TSS), hardware security (TEEs), and economic security (EigenLayer), creates a robust foundation for Okto's wallet infrastructure.
Unified User Experience
Decentralized Wallet Network (DWN) abstracts the complexity of multi-chain wallet management behind a unified, user-friendly interface. Users can:
- Log in using familiar Web2 authentication methods (e.g., Google, email, or phone).
- View and manage assets across multiple blockchains (e.g., BNB on BNB Chain, USDC on Polygon, SOL on Solana) from a single dashboard.
- Execute transactions on any supported chain through a consistent interface, without handling multiple wallets or private keys.
The DWN acts as a universal wallet layer, handling key management and transaction signing across chains. This enables developers to deliver a seamless, consistent user experience, regardless of the underlying blockchain infrastructure.
How DWN Works: Transaction Flow
To illustrate how Okto's Decentralized Wallet Network (DWN) operates, let's break down the process into two main phases. We'll use the example of a user wanting to mint an NFT.
Phase 1: Authentication & Session Registration
This phase covers how a user logs in and sets up a secure session to interact with dApps via Okto.
1. User Initiates Login
When you tap "Sign In", your client application generates a session key pair. The private key stays securely on your device, while the public key gets registered with Okto.
2. Authentication Request to the Okto Chain
Your client application, via the Okto SDK, creates an authentication request and sends it to the Okto Chain. This request bundles:
- Your authentication token (e.g., a Google OAuth token).
- The generated session public key.
- A signature created with the session private key, proving its ownership.
3. Decentralized Verification via Auth Relayer
The Okto Chain forwards the authentication request to the Auth Relayer. The Auth Relayer, utilizing a 2-of-3 Multi-Party Computation (MPC) node setup, independently verifies your credentials (e.g., the idToken) with the relevant authentication provider (like Google). A consensus among at least two of these three nodes validates your identity, ensuring no single party can spoof the authentication process.
4. Key Generation & User Setup
Once your identity is verified by the Auth Relayer, it initiates the creation of your primary blockchain keys. The Decentralized Wallet Network (DWN) generates these cryptographic keys (supporting ECDSA and EdDSA) using Distributed Key Generation (DKG). This critical process involves a 2-of-3 quorum of DWN operators.
5. On-Chain Session Registration
Finally, your session public key is registered on the Okto Chain through a User Operation (UserOp). This UserOp, often authorized by the Auth Relayer, links your active session key to your Smart Wallet Account (SWA). This linkage allows you to subsequently sign and authorize transactions using the more convenient session key.
Phase 2: Transaction Signing Flow
With an active and registered session, you can now initiate transactions. Let's continue with the "Mint NFT" example.
1. Initiate Transaction
With your session active, you tap "Mint NFT" in your dApp. The client prepares a UserOp containing the intent and session signature.
2. Submit to Okto Chain
The UserOp is sent to Okto Chain, validated, and broadcast to Okto Chain where policy checks are enforced.
3. DTN Processing
Upon validation, a job is created on the Okto chain, emitting an event for DTN to process. DTN fetches the full intent from the UserOp, constructs the raw transaction payload(s) required to execute the intent and registers its hash on the Okto chain.
4. MPC Signing via DWN Nodes
With the payloads and hashes recorded, DTN requests the DWN's Signing Service to sign these payloads using your main SWA private key. The DWN operators (the same 2-of-3 quorum) perform several critical verifications before signing. Once all verifications pass, the DWN operators collaboratively generate the required cryptographic signature(s) for the transaction(s) using MPC and a Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS).
5. On-Chain Execution
DTN receives the signed transaction from the DWN, broadcasts it to the target blockchain, and monitors the transaction status, updating the Okto Chain upon completion.
Features That Set DWN Apart
Account-Agnostic Support
Whether you use an Externally Owned Account (EOA) on Ethereum, a Solana address, a 4337 contract wallet, or social login, the DWN treats each as a "sub-account" within one universal user profile.
One Interface, Many Chains
Imagine holding BNB on BNB Chain, USDC on Polygon, and SOL on Solana. With DWN:
- Log in using familiar Web2-style methods
- View all assets across different chains on one dashboard
- Execute complex blockchain transactions with simple clicks
Embedded Wallets
Users access DWN features through embedded wallets that come in two flavors:
- Closed-Loop Wallets: Restricted to particular platforms for simplified, controlled experiences
- Interoperable Wallets: Work across various networks and platforms for broader freedom
By using Okto's SDKs, developers can easily incorporate embedded wallets into their applications, leveraging the full power of the DWN.
Getting Started with DWN
Ready to integrate DWN-powered wallets into your application?
- Explore Okto SDKs →: Multi-platform SDKs for web and mobile development
- Learn about Embedded Wallets →: Understand wallet types and interoperability